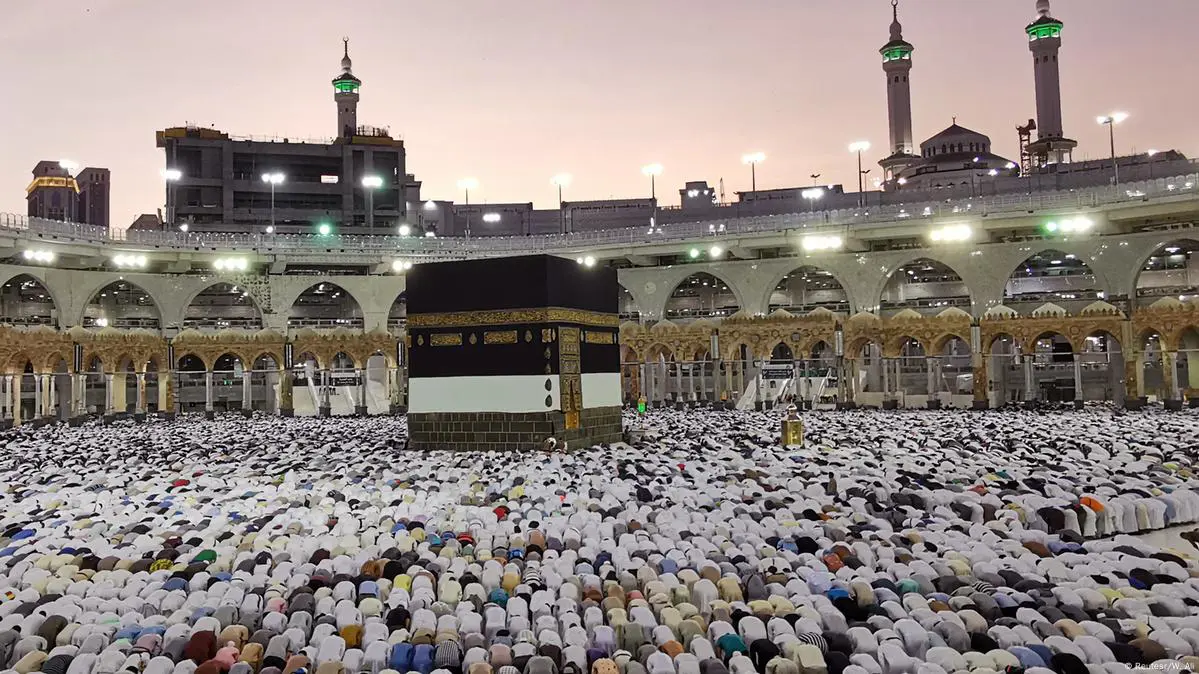

The Hajj, an annual Islamic pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia, is one of the five pillars of Islam and a spiritual obligation for every Muslim who is physically, emotionally, and financially able to undertake the journey. For millions of Muslims worldwide, Hajj 2025 represents a profound opportunity to fulfill this sacred duty, cleanse sins, and seek closeness to Allah (SWT). This comprehensive article aims to provide a detailed guide for intending pilgrims, covering everything from dates and rituals to practical preparations, health and safety, and the broader significance of this momentous event.
1.Hajj 2025: Dates, Significance, and Core Principles
Hajj 2025 is set to be a remarkable event, drawing millions of pilgrims from every corner of the globe. The exact dates for Hajj are determined by the Islamic lunar calendar, specifically taking place during the month of Dhul Hijjah, the twelfth month.
1.1 Expected Dates for Hajj 2025
While the precise dates for Hajj 2025 are subject to the sighting of the moon, current estimations indicate that the annual pilgrimage will likely occur from June 4 to June 9, 2025. The Hajj officially begins on the 8th of Dhul Hijjah and concludes on the 13th of Dhul Hijjah. This period also culminates in the joyous celebration of Eid al-Adha on the 10th of Dhul Hijjah. Pilgrims often begin their travel to Saudi Arabia in the weeks leading up to the main Hajj rituals, sometimes as early as the end of April.
Key Dates for Hajj 2025 (Tentative):
- June 4, 2025 (8th Dhul Hijjah): Hajj rituals begin in Mina.
- June 5, 2025 (9th Dhul Hijjah): Day of Arafat, the climax of the Hajj.
- June 6, 2025 (10th Dhul Hijjah): Eid al-Adha, Ramy al-Jamarat (stoning), and animal sacrifice.
- June 7-9, 2025 (11th-13th Dhul Hijjah): Further stoning rituals in Mina and completion of Hajj.
1.2 The Spiritual Significance of Hajj
The Hajj is far more than a physical journey; it is a profound spiritual journey that represents submission to Allah (SWT) and a quest for spiritual purification. It symbolizes unity among Muslims, as people from diverse backgrounds converge in Mecca to worship together. The purpose of the Hajj is multifaceted:
- Fulfillment of a Pillar of Islam: Hajj is one of the five pillars, a fundamental obligation for every capable Muslim.
- Seeking Forgiveness: Muslims believe that a properly performed Hajj can lead to the forgiveness of all past sins, making the pilgrim as pure as the day they were born. This concept of a "Mabroor Hajj" (an accepted Hajj) promises Paradise as its reward.
- Connection to Prophetic Tradition: The rituals of Hajj trace back to the traditions of Prophet Ibrahim (Abraham) and his family, and were re-established by Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him). This connection deepens the spiritual experience.
- Reinforcing Taqwa (God-Consciousness): The challenges and devotion required during Hajj strengthen a pilgrim's awareness of Allah, fostering greater piety and submission.
- Global Muslim Unity: The sight of millions of pilgrims, dressed in simple white garments, standing shoulder to shoulder, transcends racial, ethnic, and socio-economic divides, embodying the true spirit of the global Muslim community. This collective act of worship reinforces the shared identity and brotherhood of Islam.
1.3 Who is Obligated to Perform Hajj?
The obligation of Hajj applies to adult Muslims who possess:
- Physical Capacity: Good health and stamina to undertake the rigorous rituals.
- Mental Capacity: A Sound mind to understand and perform the rites.
- Financial Capacity: Sufficient funds to cover the costs of the journey for themselves and their dependents while they are away, without falling into debt.
While the obligation is once in a lifetime, Muslims are permitted and encouraged to perform Hajj more than once if they have the means.
2. Navigating the Logistics: Registration, Visas, and Packages for Hajj 2025
The logistical aspects of performing Hajj 2025 are complex and require careful planning. The Saudi Arabian government has implemented various systems to manage the influx of pilgrims, including online portals and stricter regulations.
2.1 Registration Process and Quotas
Historically, countries have been allocated quotas for the number of pilgrims they can send for Hajj. This quota system helps Saudi authorities manage crowd control and ensure adequate facilities. For Hajj 2025, authorities continue to manage pilgrim numbers effectively.
- Country-Specific Quotas: Each country with a Muslim population is allocated a specific quota, typically one pilgrim per 1,000 Muslim citizens. Major countries like Indonesia, Pakistan, India, and Bangladesh have significant quotas.
- Government and Private Schemes: Many countries offer both government-regulated Hajj schemes (often more affordable) and private Hajj packages (which can offer more luxury options). Pilgrims typically register through authorized agencies or government bodies in their home countries.
- Nusuk Hajj Platform: The Saudi government has introduced the Nusuk Hajj platform to streamline registration and visa processing. This digital portal is becoming increasingly central to the Hajj experience, allowing for faster e-visa approvals and improved management of pilgrim data. Pilgrims are advised to monitor official announcements from their respective national Hajj ministries and the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah for detailed registration procedures for Hajj 2025.
2.2 Visa Requirements for Hajj 2025
Obtaining the correct Hajj visa is paramount. The Saudi government has strict regulations regarding visas to ensure a safe and orderly pilgrimage.
- Hajj Visa Validity: Hajj visas are specific to the pilgrimage and are only valid for travel to Saudi Arabia for the purpose of Hajj. They do not permit other forms of travel or tourism within the Kingdom during the Hajj season.
- Mandatory Entry Permits for Makkah: Starting April 23, 2025, an entry permit is mandatory for all pilgrims entering Makkah, whether Saudi citizens or expatriates. Exceptions are only for individuals with Hajj permits, Makkah residents with proof of residence, and those with permits to work in the holy sites.
- Passport Validity: Pilgrims must hold a passport valid for at least six months beyond their intended stay.
- Biometric Data: The Mecca Route Initiative, active for pilgrims from countries like Indonesia, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, expedites visa issuance by collecting biometric data and issuing electronic visas before pilgrims even depart their home countries. This significantly reduces wait times upon arrival in Saudi Arabia.
- Penalties for Violations: Saudi authorities have imposed stringent penalties for individuals who violate Hajj visa regulations, including fines (up to SAR 50,000 or approximately $13,000 USD), deportation, and a potential ban from entering the Kingdom for ten years. This also applies to those who facilitate illegal pilgrims.
2.3 Hajj Packages and Costs
The cost of Hajj can vary significantly depending on the country of origin, the type of package, and the services included. Hajj packages typically cover:
- Accommodation: Hotels in Mecca and Medina, and tent accommodations in Mina and Arafat.
- Transportation: Flights to and from Saudi Arabia, as well as internal transportation between holy sites (Mecca, Medina, Mina, Arafat, Muzdalifah).
- Meals: Full or half-board meals, especially during the main Hajj days.
- Visa Fees: The cost of obtaining the Hajj visa.
- Guided Services: Often include experienced Hajj guides who assist pilgrims with rituals and provide support.
Factors Influencing Hajj Costs:
- Accommodation Proximity: Hotels closer to the Haram (Grand Mosque) in Mecca and the Prophet's Mosque in Medina are generally more expensive.
- Hotel Star Rating: Luxury packages with 5-star hotels will be significantly pricier than more basic options.
- Occupancy: Quadruple (four people per room), triple, and double occupancy rates will impact the per-person cost.
- Duration of Stay: Longer packages generally incur higher costs.
- Services Included: Comprehensive packages that cover everything from flights to full board meals and dedicated medical support will be more expensive.
Pilgrims are strongly advised to research reputable and accredited travel agencies well in advance for the Hajj 2025. Early booking is crucial to secure preferred accommodation and Hajj packages, especially given the expected record number of pilgrims. It is also important to ensure that the chosen package complies with all governmental regulations.
3. Essential Preparations for Hajj 2025: Physical, Spiritual, and Practical
A successful Hajj experience hinges on thorough preparation, encompassing physical, spiritual, and practical aspects. This journey demands immense endurance and devotion, making pre-departure planning vital.
3.1 Physical Preparation
The Hajj rituals involve significant walking and physical exertion, especially during the days in Mina, Arafat, and Muzdalifah. Pilgrims should prioritize their physical health.
- Fitness Regimen: Start a regular exercise routine, including daily walks or light cardio, at least six months before departure. This will build stamina for the long distances covered during Tawaf, Sa'i, and movement between sites.
- Health Check-up: Consult a doctor for a comprehensive health check-up. Pilgrims with pre-existing medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, heart disease, chronic lung disease) should seek medical advice on managing their conditions during the pilgrimage.
- Vaccinations: Mandatory vaccinations include:
- Quadrivalent Meningococcal (ACWY) Conjugate Vaccine: Valid for 5 years.
- COVID-19 Vaccination: Proof of immunization is required, either a single dose of the updated 2024-2025 vaccine or completion of the primary series (2021-2023) or laboratory-confirmed recovery from COVID-19 in 2024.
- Influenza Vaccination: Must be received within 12 months before travel.
- Other Recommended Vaccines: Depending on the pilgrim's health and origin country, pneumococcal, MMR, varicella, and hepatitis B vaccines may be recommended.
- Medication: Carry an adequate supply of personal medications with valid prescriptions. It's advisable to have prescriptions written by a doctor that can be shown to local clinics in Saudi Arabia if needed.
- Heat Acclimatization: Saudi Arabia's summer temperatures can be extreme. Pilgrims should prepare for heat and humidity, ensuring they stay hydrated and protect themselves from the sun.
3.2 Spiritual Preparation
The spiritual dimension of Hajj is paramount. Pilgrims should prepare their hearts and minds for this sacred journey.
- Intention (Niyyah): Ensure the intention for Hajj is pure, solely for the sake of Allah (SWT).
- Study and Understanding: Learn about the Hajj rituals, their order, and their spiritual significance. Reading books, attending seminars, and watching educational videos can deepen understanding.
- Repentance and Forgiveness: Seek forgiveness for past sins, reconcile with others, and settle any outstanding debts or grievances before embarking on the journey.
- Increase Acts of Worship: Engage in extra prayers (Salah), supplications (Dua), recitation of the Quran, and remembrance of Allah (Dhikr) to build spiritual strength.
- Patience and Humility: Prepare for challenges, crowds, and potential discomfort with patience and humility, embracing the spirit of sacrifice inherent in Hajj.
3.3 Practical Packing List
A well-organized packing list ensures comfort and addresses practical needs during the Hajj experience.
Essential Documents:
- Passport with valid Hajj visa
- Vaccination certificates (Yellow Card)
- Airline tickets and booking confirmations
- Hajj package details and agency contact information
- Proof of financial ability (if required)
- Copies of all important documents (keep digital copies as well)
Clothing and Footwear:
- Ihram attire (for men): Two unstitched white pieces of cloth. Carry extra sets.
- Modest clothing (for women): Loose-fitting abayas, hijabs, and inner garments. Carry extra sets.
- Comfortable walking shoes or sandals (that meet Hajj requirements for Ihram).
- Socks (waterproof wudu socks can be useful).
- Lightweight jacket for cooler evenings.
- Breathable sleepwear.
- Small, foldable prayer mat.
- Hat or scarf with underscarf caps for sun protection.
Toiletries and Personal Items (unscented for Ihram):
- Unscented soap, shampoo, lotion.
- Toothbrush and miswak.
- Small towel.
- Sanitizer.
- Tissues.
- Nail clippers.
- Small mirror.
Health and Wellness:
- Personal medications (with prescriptions).
- Basic first-aid kit (band-aids, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, blister treatment).
- Electrolyte packets/oral rehydration salts.
- Sunscreen.
- Lip balm.
- Small, portable fan.
- Masks (especially for crowded areas).
Other Useful Items:
- Small, lightweight backpack for daily essentials.
- Waist belt or pouch for valuables.
- Reusable water bottle (many hotels and mosques have refill stations).
- Snacks (non-perishable, easy to carry).
- Portable power bank for electronics.
- Smartphone with Hajj apps (for navigation, Quran, duas).
- Earplugs (for noisy environments).
- Small flashlight.
- Small umbrella for sun protection.
- Plastic bags for shoes during prayers.
- Pen and a small notebook/diary for reflections.
4. The Journey of Hajj: Rituals and Steps
The Hajj pilgrimage is a series of meticulously performed rituals that span several days. Understanding each step is crucial for a meaningful and correct performance of the Hajj.
4.1 Ihram: The State of Purity
The Hajj begins with entering the state of Ihram, a sacred state of purity.
- Intention: Making the intention to perform Hajj.
- Ghusl (ritual bath): Recommended before entering Ihram.
- Ihram Garments:
- Men: Two pieces of unstitched white cloth.
- Women: Any loose, modest clothing, typically an abaya, with a head covering, leaving the face and hands uncovered.
- Prohibitions in Ihram: Certain actions become prohibited, including cutting hair or nails, using scented products, hunting, engaging in sexual activity, and arguing.
Pilgrims enter Ihram at designated points called Meeqat, usually upon arrival at Jeddah or Medina airport, depending on their itinerary.
4.2 Tawaf and Sa'i in Mecca
Upon reaching Mecca, pilgrims proceed to the Grand Mosque (Masjid al-Haram) to perform the initial rituals.
- Tawaf al-Qudoom (Arrival Tawaf): Circling the Kaaba seven times counter-clockwise, starting and ending at the Black Stone (Hajar al-Aswad).
- Sa'i: Walking seven times between the hills of Safa and Marwah, commemorating Hajar's (Hagar's) desperate search for water for her son Isma'il (Ishmael).
4.3 Journey to Mina: The Tent City
On the 8th of Dhul Hijjah, pilgrims travel to Mina, a vast tent city located a few kilometers outside Mecca.
- Day of Tarwiyah (Watering): Pilgrims spend the day in Mina, praying, reflecting, and preparing for the Day of Arafat. The air-conditioned tents in Mina provide a basic but comfortable setting for pilgrims.
4.4 Standing at Arafat: The Climax of Hajj
The 9th of Dhul Hijjah, the Day of Arafat, is considered the most significant day of Hajj.
- Waqf al-Arafat (Standing at Arafat): Pilgrims spend the entire day from noon until sunset on the plain of Arafat, standing in devotion, making sincere supplications (Dua), and seeking Allah's forgiveness. Mount Rahma (Mount of Mercy) is a significant spot here. This is the spiritual pinnacle of the Hajj, and missing this standing invalidates the entire Hajj.
4.5 Muzdalifah: Collecting Pebbles
After sunset on the Day of Arafat, pilgrims depart for Muzdalifah.
- Night in Muzdalifah: Pilgrims spend the night under the open sky in Muzdalifah, collecting pebbles for the symbolic stoning ritual (Ramy al-Jamarat) that follows.
4.6 Ramy al-Jamarat, Sacrifice, and Halq/Taqsir: The Day of Eid
The 10th of Dhul Hijjah marks Eid al-Adha and several important rituals.
- Ramy al-Jamarat: Pilgrims return to Mina and perform the symbolic stoning of the devil by casting seven pebbles at the largest pillar, Jamarat al-Aqaba. This commemorates Prophet Ibrahim's rejection of Satan's temptations.
- Animal Sacrifice: Pilgrims offer an animal sacrifice (usually a lamb or goat), symbolizing Prophet Ibrahim's willingness to sacrifice his son Isma'il in obedience to Allah. This sacrifice is often managed through coupons or authorized slaughterhouses.
- Halq (shaving) or Taqsir (trimming): Men shave their heads (Halq), while women trim a small portion of their hair (Taqsir). This signifies partial exit from the state of Ihram.
- Tawaf al-Ifadah: Pilgrims return to the Grand Mosque in Mecca to perform another circumambulation of the Kaaba, the Tawaf al-Ifadah. This signifies a deeper purification and is a key pillar of Hajj.
4.7 Days of Tashreeq: Continued Stoning and Departure
The 11th, 12th, and optionally 13th of Dhul Hijjah are known as the Days of Tashreeq.
- Continued Ramy: Pilgrims remain in Mina and perform the stoning of all three Jamarat pillars (small, medium, and large) on each of these days.
- Farewell Tawaf: Before departing Mecca, pilgrims perform a final circumambulation of the Kaaba, the Tawaf al-Wida (Farewell Tawaf), marking the conclusion of their pilgrimage.
5. Health, Safety, and Well-being during Hajj 2025
Given the massive crowds and demanding conditions, health and safety are paramount concerns for pilgrims and Saudi authorities alike.
5.1 Health Guidelines and Precautions
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is critical, especially in the hot climate. Pilgrims should carry and drink plenty of water.
- Hygiene: Practicing good personal hygiene, including frequent handwashing, is essential to prevent the spread of illness in crowded environments.
- Foot Care: Comfortable footwear is crucial, and pilgrims should attend to any blisters or foot pain promptly.
- Avoiding Overexertion: While Hajj is demanding, pilgrims should rest whenever possible and avoid unnecessary exertion.
- Medical Facilities: Saudi Arabia provides extensive medical services during Hajj, including clinics, hospitals, and emergency services at the holy sites. Pilgrims should familiarize themselves with the location of medical aid.
- Masks: Wearing masks in crowded places is advisable to prevent respiratory infections.
5.2 Safety and Crowd Management
The Saudi government has invested heavily in infrastructure and technology to ensure the safety and efficient management of millions of pilgrims.
- Crowd Control Measures: Staggered movement schedules, AI-powered crowd control systems, and enhanced entry/exit systems at the Grand Mosque and Jamarat bridge help manage the flow of pilgrims.
- Hajj Smart ID Bracelets: These wearable devices store essential pilgrim data, including personal information and medical records, aiding in real-time tracking, emergency alerts, and providing necessary support.
- Security Personnel: A significant presence of security personnel ensures order and safety throughout the pilgrimage sites.
- Emergency Services: Mobile clinics, ambulances, and emergency response teams are strategically positioned to provide rapid assistance.
- Prohibited Items: Firearms, sharp objects, alcohol, illegal drugs, and environmentally harmful materials (like certain plastics) are strictly prohibited for safety and compliance.
5.3 Environmental Considerations and Green Hajj Initiatives
The sheer scale of Hajj presents environmental challenges. The Saudi government and various organizations are promoting a "Green Hajj" initiative.
- Waste Management: Pilgrims are encouraged to dispose of waste in designated bins, avoid single-use plastics, and engage in green activities.
- Eco-Friendly Transportation: Utilizing public transport systems like the Haramain High-Speed Railway (connecting Mecca and Medina) and carpooling can reduce carbon emissions. Walking when possible is also encouraged.
- Water Conservation: Conserving water is crucial in the arid region. Pilgrims should practice efficient ablution and report any water leaks.
- Energy Conservation: Choosing energy-efficient accommodations, turning off lights and electronics when not in use, and using natural light can contribute to energy savings.
- Digital Resources: Using digital copies of the Quran, Duas, and guidebooks instead of paper versions reduces waste.
6. Accommodation and Transportation for Hajj 2025
Careful planning for accommodation and transportation is crucial for a comfortable and efficient Hajj experience.
6.1 Accommodation in Mecca and Medina
Pilgrims typically spend time in both Mecca and Medina.
- Mecca: Hotels near the Grand Mosque (Masjid al-Haram) are highly sought after. These range from luxury 5-star establishments to more budget-friendly options. Proximity to the Haram is a major factor in pricing and convenience.
- Medina: Hotels near the Prophet's Mosque (Masjid an-Nabawi) are also popular. Many pilgrims begin their journey in Medina to visit the Prophet's Mosque and other historical sites before proceeding to Mecca for the main Hajj rituals.
- Mina and Arafat: During the Hajj days, pilgrims stay in large, air-conditioned tents in Mina and Arafat. These tent cities are equipped with basic facilities, including kitchens and prayer areas. The Saudi government has been upgrading these tents to include features like sofa-cum-beds and improved air conditioning.
- Accommodation Regulations: The Ministry of Tourism in Saudi Arabia has instructed all hospitality establishments in Makkah to avoid providing accommodation to individuals1 without a Hajj permit or official entry permit during the Hajj season, reinforcing the strict regulations.
individuals
Efficient transportation systems are vital for moving millions of pilgrims between the holy sites.
- Intercity Travel: The Haramain High-Speed Railway connects Mecca and Medina, offering a fast and convenient travel option.
- Within Holy Sites: During the main Hajj days (Mina, Arafat, Muzdalifah), buses are the primary mode of transportation. There are extensive bus networks, and luxury buses are provided for pilgrims in higher-end packages.
- Makkah Metro: The Makkah Metro plays a crucial role in reducing congestion between Mina, Arafat, and Muzdalifah, especially during the peak days of Hajj.
- Smart Traffic Management: AI-powered systems are used to regulate vehicle movement and optimize traffic flow.
- Shuttle Services: Many Hajj packages include dedicated shuttle services between hotels and the Grand Mosque, and for movement during the rituals.
7. The Cultural Impact and Evolution of Hajj
The Hajj is not just a religious obligation; it is a significant cultural event that shapes the lives of pilgrims and has a profound impact on the global Muslim community.
7.1 Cultural Exchange and Brotherhood
- Diversity: The annual pilgrimage brings together Muslims from diverse linguistic, ethnic, and cultural backgrounds, fostering a unique environment of global brotherhood and unity.
- Shared Experience: Despite differences, pilgrims share a common purpose and experience, creating bonds that often last a lifetime. This shared spiritual journey transcends national borders and reinforces the concept of the Ummah (global Muslim community).
- Cultural Learning: Pilgrims often learn about different Islamic traditions, customs, and ways of life from fellow pilgrims, enriching their understanding of the broader Muslim world.
7.2 Historical Context and Evolution
The Hajj has a rich history dating back thousands of years to Prophet Ibrahim (peace be upon him) and was re-established by Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) in 628 CE. Over centuries, the logistics and infrastructure of Hajj have evolved dramatically.
- Early Pilgrimages: In earlier times, the journey to Mecca was arduous and dangerous, often taking months or even years. Pilgrims traveled in caravans, facing desert perils, disease, and banditry.
- Modernization: In recent decades, the Saudi government has invested billions in modernizing Hajj infrastructure, including expanding the Grand Mosque, building high-speed railways, improving tent cities, and implementing advanced crowd management technologies. This has transformed the pilgrimage, making it safer and more accessible.
- Technological Integration: The introduction of smart ID bracelets, interactive Hajj apps, and online registration platforms showcases the role of technology and innovation in improving the Hajj experience.
7.3 Economic Impact
The Hajj also has a significant economic impact on Saudi Arabia.
- Tourism Revenue: The influx of millions of pilgrims generates substantial tourism revenue for the Kingdom.
- Hospitality and Services: The pilgrimage season creates a surge in demand for accommodation, transportation, food services, and retail, boosting job opportunities and local economies.
- Infrastructure Development: The continuous investment in Hajj infrastructure drives construction and development projects across the country.
8. Addressing Challenges and Future Outlook for Hajj 2025 and Beyond
While significant progress has been made, the Hajj still presents unique challenges, especially with the anticipated record number of pilgrims for Hajj 2025.
8.1 Common Hurdles for Pilgrims
- Overcrowding: Despite advanced crowd management, the sheer volume of pilgrims can still lead to immense crowding, especially during peak rituals like Tawaf and Ramy al-Jamarat.
- Heat and Dehydration: The summer climate in Saudi Arabia poses a significant risk of heat exhaustion and dehydration.
- Fatigue: The physical demands and long hours can lead to extreme fatigue.
- Communication Barriers: Language differences can sometimes be a challenge, though services are increasingly available in multiple languages.
8.2 Solutions and Initiatives by Saudi Authorities
The Saudi government is continuously implementing solutions to enhance the Hajj experience.
- Expansion Projects: Ongoing expansion of the Grand Mosque and surrounding areas aims to increase capacity for worshippers.
- Technological Solutions: Continued integration of technology like AI-powered crowd control, digital Hajj permits, and smart navigation apps.
- Medical Preparedness: Increased medical staff, mobile clinics, and emergency services to address health issues quickly.
- Logistical Efficiency: Improved transportation networks, including enhanced bus services and metro expansion, to ensure smooth movement of pilgrims.
- "Green Hajj" Initiatives: Efforts to make the pilgrimage more environmentally sustainable by reducing waste and promoting eco-friendly practices.
8.3 The Future of Hajj
The future of Hajj is likely to see continued advancements in technology and innovation, further infrastructure development, and a greater emphasis on sustainability. The goal remains to ensure that every Muslim who is able to perform Hajj can do so safely, comfortably, and with maximum spiritual benefit. Initiatives like the Nusuk platform are paving the way for a more digital and streamlined Hajj journey.
9. Personal Stories and Reflections on the Hajj Experience
For those who have undertaken the Hajj, it is often described as a life-altering spiritual journey. Personal stories highlight the transformative power of this annual pilgrimage.
- Overcoming Challenges: Many pilgrims recount the physical and mental challenges they faced and how overcoming them strengthened their faith and resilience.
- Sense of Unity: The profound sense of unity and brotherhood experienced while performing rituals alongside millions from diverse backgrounds is a recurring theme in pilgrim narratives.
- Spiritual Rejuvenation: The experience of standing on Arafat, supplicating to Allah, and performing the Tawaf around the Kaaba often leaves pilgrims with a deep sense of peace, humility, and spiritual rejuvenation.
- Post-Hajj Life: Many pilgrims describe a significant shift in their priorities and lifestyle after returning from Hajj, often leading to a greater commitment to their faith and community.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Hajj 2025
To further assist intending pilgrims, here are some frequently asked questions about Hajj 2025:
Q1: When exactly is Hajj 2025 expected to take place?
A1: Hajj 2025 is expected to begin on June 4, 2025, and end on June 9, 2025, pending official moon sighting confirmation from Saudi Arabia.
Q2: Is there an age restriction for Hajj 2025?
A2: Children under the age of 12 are generally not permitted to perform Hajj. There is no upper age limit, though medical clearance might be required for elderly pilgrims.
Q3: Can women perform Hajj without a male guardian (mahram) for Hajj 2025?
A3: Traditionally, women require a mahram. However, some contemporary interpretations and government policies may vary. It's essential to check the latest guidelines from the Saudi Ministry of Hajj and Umrah and your national Hajj authorities.
Q4: What vaccinations are mandatory for Hajj 2025?
A4: Mandatory vaccinations include the Quadrivalent Meningococcal (ACWY) Conjugate Vaccine, COVID-19 vaccine (updated 2024-2025 season or primary series), and influenza vaccine (within 12 months of travel).
Q5: How can I check the status of my Hajj visa?
A5: You can typically check your Hajj visa status through the Hajj itinerary section in your Nusuk account or through your authorized Hajj travel agency.
Q6: What is the "Mecca Route Initiative"?
A6: The Mecca Route Initiative is a program by the Saudi government to facilitate pilgrims' entry by completing visa, health, and luggage procedures at their departure airports in select countries (e.g., Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh) before they even reach Saudi Arabia, streamlining the arrival process.
Q7: How much will Hajj 2025 cost?
A7: The cost of Hajj 2025 varies widely depending on the country of origin, the type of package (basic, standard, luxury), accommodation quality and proximity, and services included. It can range from basic packages to premium options costing upwards of USD 15,000.
Q8: What should I do if I have a medical emergency during Hajj?
A8: Saudi Arabia has extensive medical facilities, including mobile clinics and hospitals, throughout the holy sites. Pilgrims should carry their Hajj Smart ID Bracelet, which contains essential medical information, and seek immediate medical attention if needed.
Q9: Are there any environmentally friendly practices encouraged during Hajj?
A9: Yes, pilgrims are encouraged to participate in the "Green Hajj" initiative by minimizing waste, conserving water, using public transport, and reducing energy consumption.
Q10: What is the significance of Medina for pilgrims?
A10: While not part of the Hajj rituals themselves, Medina is the second-holiest city in Islam and home to the Prophet's Mosque, where Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) is buried. Many pilgrims visit Medina before or after the Hajj to pray in the mosque and connect with early Islamic history.
Hajj 2025 promises to be an exceptional and deeply moving experience for millions of Muslims. With meticulous planning, spiritual devotion, and adherence to guidelines, pilgrims can embark on this sacred journey to Mecca and fulfill one of the most profound obligations in Islam.
;More Travel News
-
 30-Oct-2025How to Choose Between a Beach Villa & Overwater Villa in the Maldives
30-Oct-2025How to Choose Between a Beach Villa & Overwater Villa in the Maldives -
 16-Aug-2025Massive Landslides, Flash Floods Imperil Tourists in North — Authorities Warn Against Travel
16-Aug-2025Massive Landslides, Flash Floods Imperil Tourists in North — Authorities Warn Against Travel -
 14-Dec-2022Saudi Arabia Tourist Visa
14-Dec-2022Saudi Arabia Tourist Visa -
 01-Jul-2020European Union Bans Pakistani Airline Flights Due To Safety Issues
01-Jul-2020European Union Bans Pakistani Airline Flights Due To Safety Issues -
 12-Aug-2021This Is How UAE Residents Can Check Their Visa Validity To Return Home
12-Aug-2021This Is How UAE Residents Can Check Their Visa Validity To Return Home -
 23-Oct-201910 Cheapest Umrah Packages in Pakistan
23-Oct-201910 Cheapest Umrah Packages in Pakistan -
 27-Jul-2023Saudi Arabia has ended the sticker visa system on passports for 12 countries
27-Jul-2023Saudi Arabia has ended the sticker visa system on passports for 12 countries -
 15-Dec-2022UAE Changes Visit Visa Extension Policy
15-Dec-2022UAE Changes Visit Visa Extension Policy -
 06-Aug-2025The UAE's 5-Year Multiple Entry Visa
06-Aug-2025The UAE's 5-Year Multiple Entry Visa -
 12-Mar-2025Flight & Hotel Prices Surge for Ramzan 2025 Umrah – Book Early to Save
12-Mar-2025Flight & Hotel Prices Surge for Ramzan 2025 Umrah – Book Early to Save -
 08-Nov-2024Flying to Thailand What You Need to Know About the New Visa Rules
08-Nov-2024Flying to Thailand What You Need to Know About the New Visa Rules -
 06-May-2025Portugal Fast-Track Work Visa for Foreign Workers Guide for May 2025
06-May-2025Portugal Fast-Track Work Visa for Foreign Workers Guide for May 2025
